Catamenia refers to the menstrual cycle.
Just like the menstrual cycle that happens every 30 days for most women, certain afflictions affect women on a monthly basis. Thankfully, they are not very common but when they happen, they can be quite serious and even live threatening for those affected. Let’s talk about this and other common and potentially very serious problems that affect women in a cyclical manner.
Women have their periods every single month due to the cyclical nature of hormones, secreted by the pituitary to which the ovary responds and produces oestrogen and progesterone in a cyclical manner. Sudden withdrawal of the stimulation from the pituitary gland, leads to the degeneration of the innermost lining of the uterus call the endometrium and its expulsion outside along with blood, and this is what constitutes the menses.
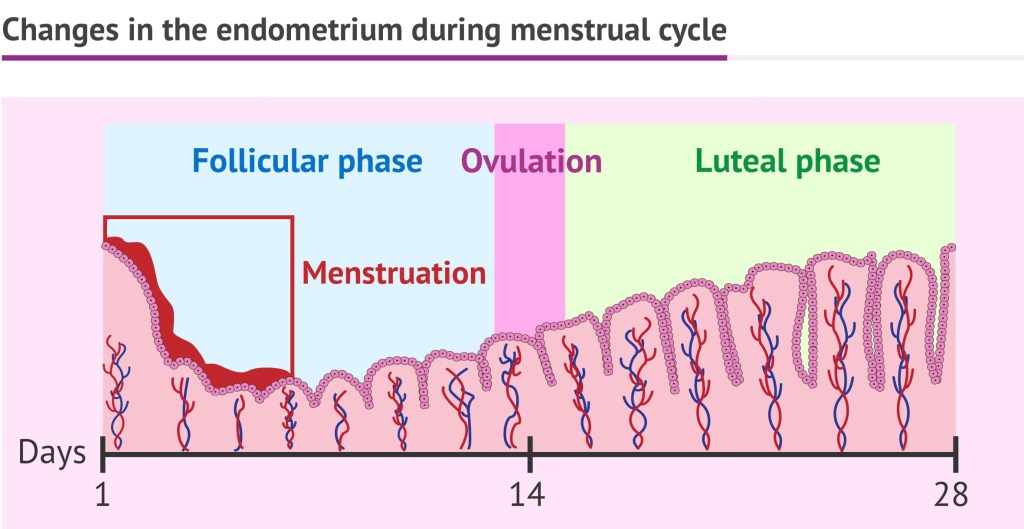
Under the effect of the same hormones, some women suffer from the following conditions:
1. Dysmenorrhea
2. Premenstrual syndrome – premenstrual tension and premenstrual dysphoric disorder.
3. Cyclical oedema of women
4. Catamenial epilepsy
5. Catamenial Migraine.
6. Catamenial Pneumothorax
7. Catamenial Anaphylaxis
1. Dysmenorrhea – or painful menstruation is a common problem for women in their reproductive years. When severe it can seriously impair the quality of life and affect daily activities. Primary dysmenorhea occurs in the absence of pelvic disease in adolescents and young women. Secondary dysmenorrhea occurs in the presence of other pelvic disease such as endometriosis, adenomyosis or fibroids. Dysmenorrhea can also occur in the presence of pelvic infection (pelvic inflammatory disease).
Treatment would include simple analgesic (paracetamol) and NSAIDs (non steroidal antiinflammatory drugs such as Ibuprofen, Mefanemic acid and Naproxen) to start with. TENS (transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation) and hormonal therapies (oral contraceptive pills) may be tried.
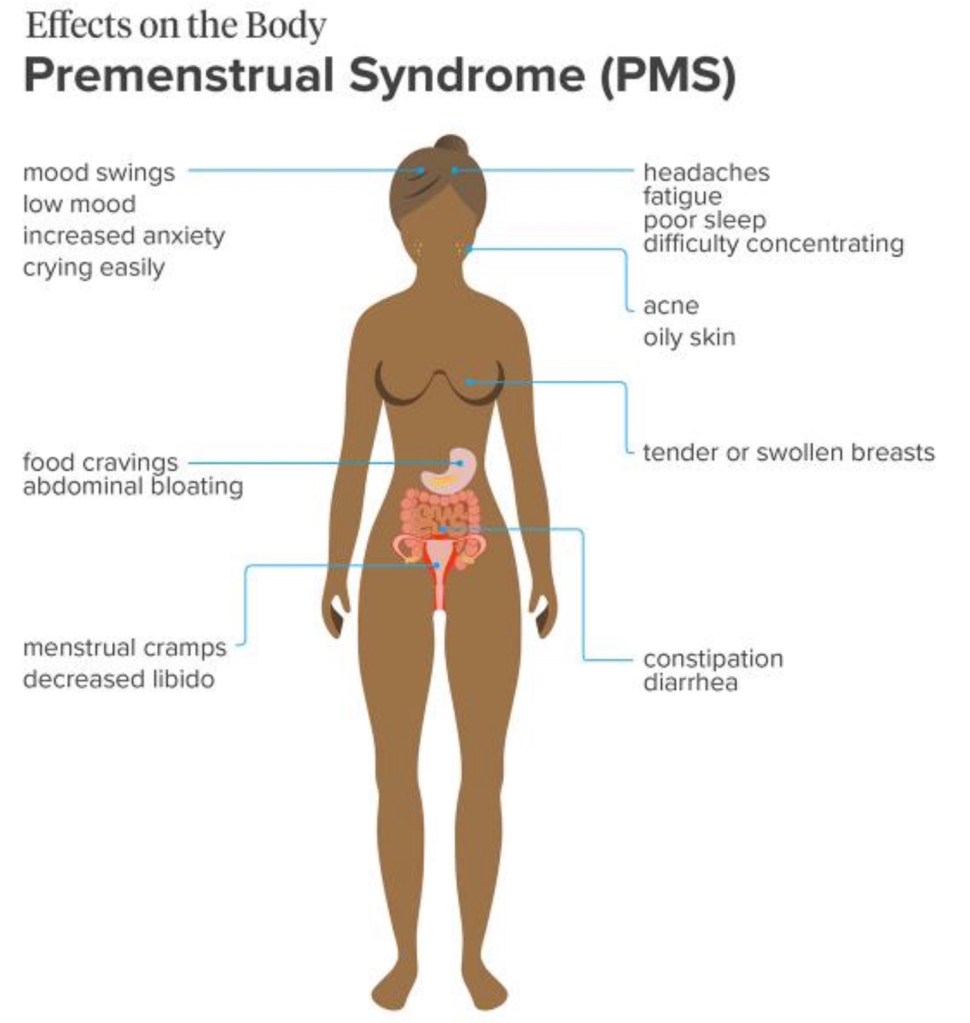
2. Premenstrual tension syndrome: refers to the physical and psychological symptoms that start anywhere from a few days to 2 weeks before the onset of the menses. The symptoms include mood swings, food cravings, fatigue, irritability, depression, sadness, crying loss of interest in sex and breast tenderness and bloating.
Treatment: these symptoms can be reduced by taking up to 2 gram of calcium per day and magnesium supplementation and by reducing water intake. Vitamin E can also be useful.
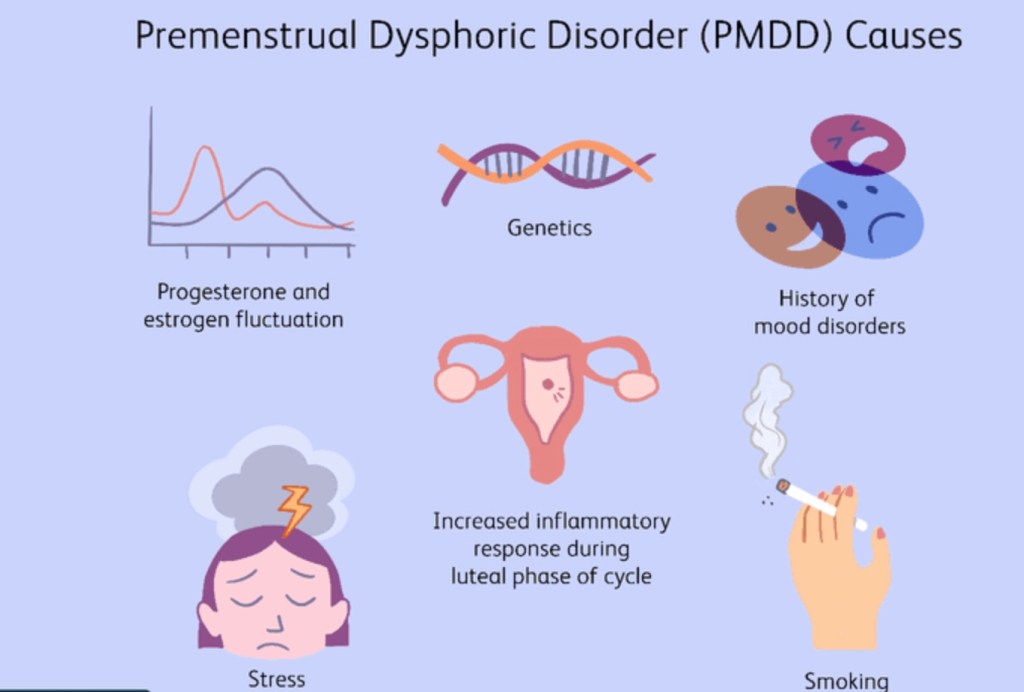
Premenstrual dysphoric disorder: PMDD refers to severe disabling mood swings and is considered a severe form of pre-menstrual (tension) syndrome. Often the physical and behavioural symptoms do not resolved with the onset of menses. Symptoms in addition could include anxiety and panic attacks, suicidal thoughts, headaches and insomnia. SSRI antidepressants and combined oral contraceptive pills may be prescribed along with cognitive behaviour techniques provided by a counselling psychologist.
3. Cyclical oedema of women refers to retention of fluid in the orthostatic position I.e., in the standing position. People develop swelling of the face, hands, breasts, abdomen and legs with a real weight gain; all made worse during the day time when the person is standing and moving about. This weight gain can be as high as 4 kgs in 24 hrs. Ladies with this condition may experience facial swelling on waking up in the morning or difficulty in removing their rings from their fingers. This extra water retention responds to the use of diuretics (spironolactone) and reduced time standing.
4. Catamenial Epilepsy– up to 40% of women have a worsening of seizures in relation to their menstrual cycle. Although rare it happens under the influence of the female hormones. It can happen throughout the cycle but based on the time of occurrence it is divided into three types. C1 refers to perimenstrual seizures. C2 refers to seizures that happen at a time of ovulation, in the middle of the cycle. C3 refers to what happens during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle.
About 75% of all seizures occur in a 10 day period, four days before and six days after the onset of menses. It is thought that withdrawal of progesterone derived GABAminergic neuro steroids triggers off the seizures. The seizures could either be partial or generalised. The seizures are primarily treated with anti-epileptic drugs but when they can’t be controlled combined contraceptive pills may be added.
5. Catamenial migraine: refers to the occurrence of a worsening headache around the time of the menstrual period. It usually occurs within two days before or three days after the periods. It is believed to occur due to a drop in the estrogen levels. It is quite similar to migraine happening at any other time. It could be associated with aura or not. 60% of migraine headaches could occur around the time of the periods.
Treatment includes NSAIDS, beta-blockers, tricyclic antidepressants and ergotamines and tryptans – just like migraine treatments at any other time.
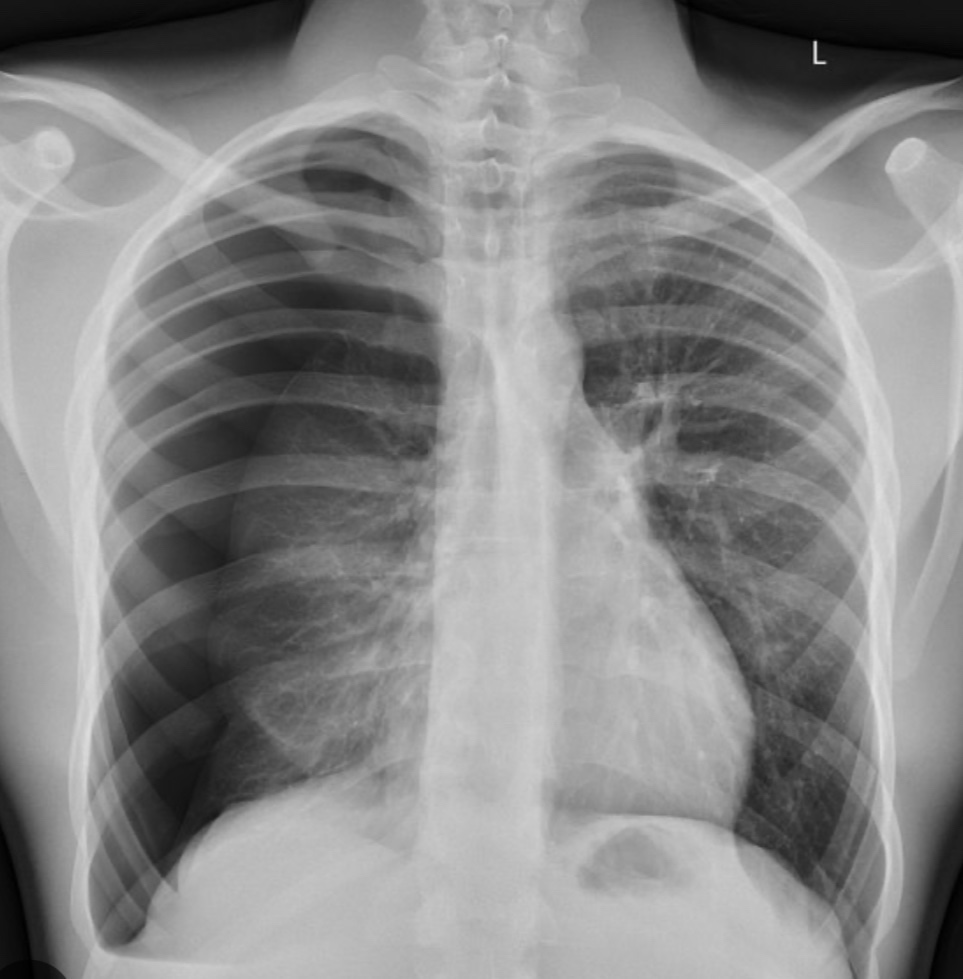
6. Catamenial Pneumothorax: this refers to the recurrent accumulation of air in the pleural cavity in women of reproductive age in the absence of concomitant respiratory disease. Typically pneumothorax occurs 72 hours before or after the periods. It caused by the implantation of ectopic endometrial tissue in the pleural space,as a part of endometriosis. It caused pneumothorax more often on the right side. To make this diagnosis it is necessary to have two episodes of pneumothorax associated with menses.
Treatment- take me to include Pleurodesis, surgery to resect out the endometrial tissue adherent to the pleura followed by oral contraceptive pill treatment.
7. Catamenial Anaphylaxis – refers to a rare anaphylactic syndrome occurring during the second phase of menstruation and is characterised by dermatitis, urticaria, angio oedema and asthma and cardiovascular collapse. It usually happens before menstruation and is believed to occur due to hypersensitivity to progesterone and to the vasoactive component in menstrual fluid such as prostaglandins. Most tests of anaphylaxis such as complement assays, serum tryptase and tests for carcinoid and phaeochromocytoma usually return negative.
Treatment – Indomethacin which inhibits prostaglandins is beneficial.
With so many problems happening monthly, it is essential for all women to have a good gynaecologist to help them cope with effective treatments.










You must be logged in to post a comment.